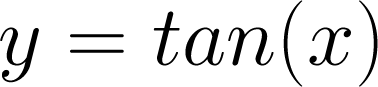
In the following examples, follow these steps:
- Draw the XY-axis with your EZ Graphing slide case.
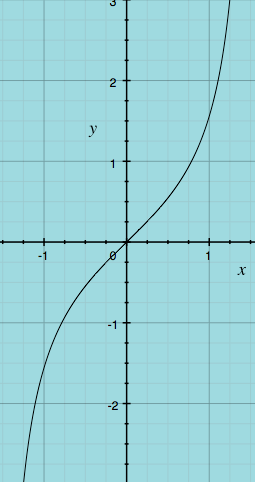
- Graph the parent function.
- Now add to your graph Reflection, Dilation and Translation in this order.
- Finally, click on the problem to check the solution.
General Form for Tangent Curves
A = This is the y-dilation of the curve. Tip: Tangent curves do not have “Amplitudes.”
B = Frequency; in a way, this is the x-dilation of the curve. This important value helps you find the period of the tangent curve:
C = Translation in the x-axis; also known as the phase shift
D = Translation in the y-axis
Translation
Example 1
Example 2
Dilation
Example 3
Example 4
Example 5
Reflection
Example 7
Example 8
Put it all together
Example 9
Example 10
